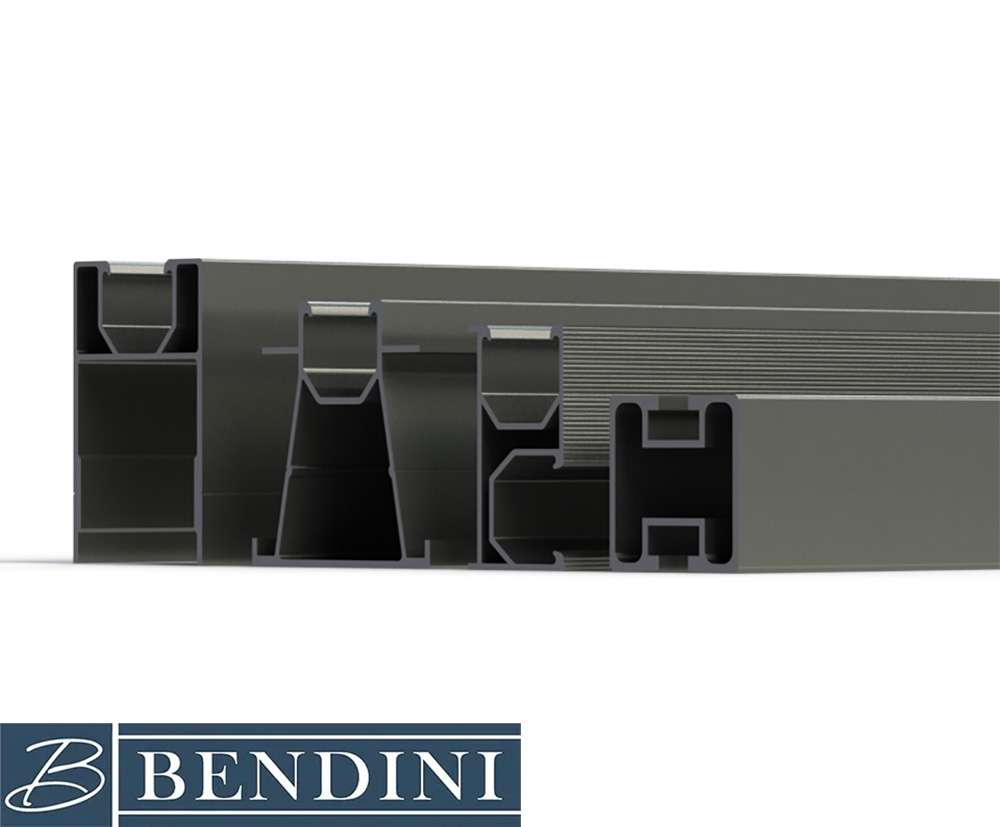
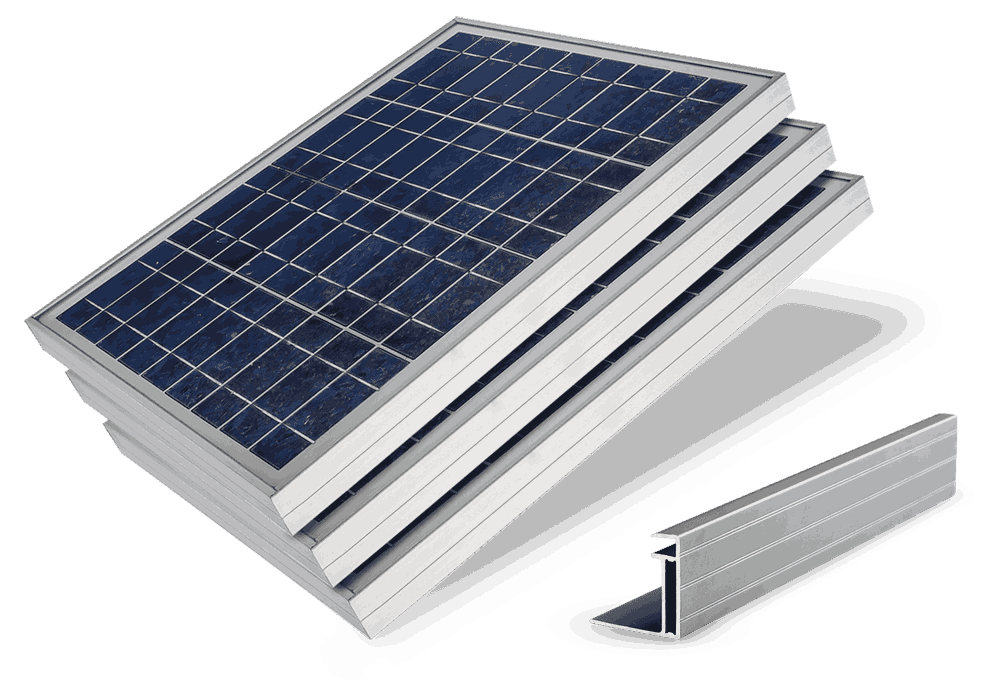
Solar Panel System
In a solar panel system, aluminum profiles are considered one of the key components. These profiles are responsible for holding and supporting the panels in their installation position. Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, which ensures the long-term stability of the structure. Moreover, due to its lightness and ease of cutting and drilling, installation is faster. In addition, it is highly resistant to environmental factors such as humidity, rain, snow, and UV radiation.
The advantages of using aluminum in solar panel systems
- Lightweight (easy to transport)
- Rust-resistant and suitable for humid or coastal areas
- Recyclable and environmentally friendly
- Long lifespan (over 25 years)
- Low maintenance requirements

To receive professional advice, please complete the form below


The commonly used types of profiles in solar panel structures
- Rail Profile: Used for directly holding the panels (similar to T or C shapes).
- Bracket/Clamp Profile: Used to secure the corners of panels or hold them at an angle.
- Base Profile: Used to connect the rails to the ground or roof.
- Tilted Mounts Profile: Used for installation at the proper angle relative to the sun.
Order Your Solar Panel System
Applications of Solar Panels
Solar panels have found a wide range of applications in recent years. Depending on the type of need and geographical location, they are used in various areas. The main applications include:
Residential
Electricity generation for homes (lighting, appliances, HVAC systems).
Standalone solar panel systems in rural areas or places without access to the power grid.
Solar water heaters for domestic hot water supply.
Commercial and Industrial
Supplying energy to factories, workshops, and stores to reduce electricity costs.
Agricultural applications: solar water pumps, drip irrigation systems.
Infrastructure and Transportation
Powering traffic signals, streetlights, and CCTV cameras on roads.
Charging stations for electric vehicles.
Use in solar-powered vehicles (buses, boats, or even small cars).
Remote and Emergency Areas
Providing energy for camps, border posts, telecom towers, and field hospitals.
Use in disaster situations (earthquakes, floods) to generate emergency electricity.
Large-Scale Integration (Solar Power Plants)
Solar power plants in deserts and sunny regions, where thousands of panels are installed and the generated electricity is fed into the national grid.
Small and Portable Devices
Solar chargers for mobile phones and laptops.
Portable lights and lighting devices.
Wearable gadgets and solar-powered watches.



